Uterine polyps (endometrium)
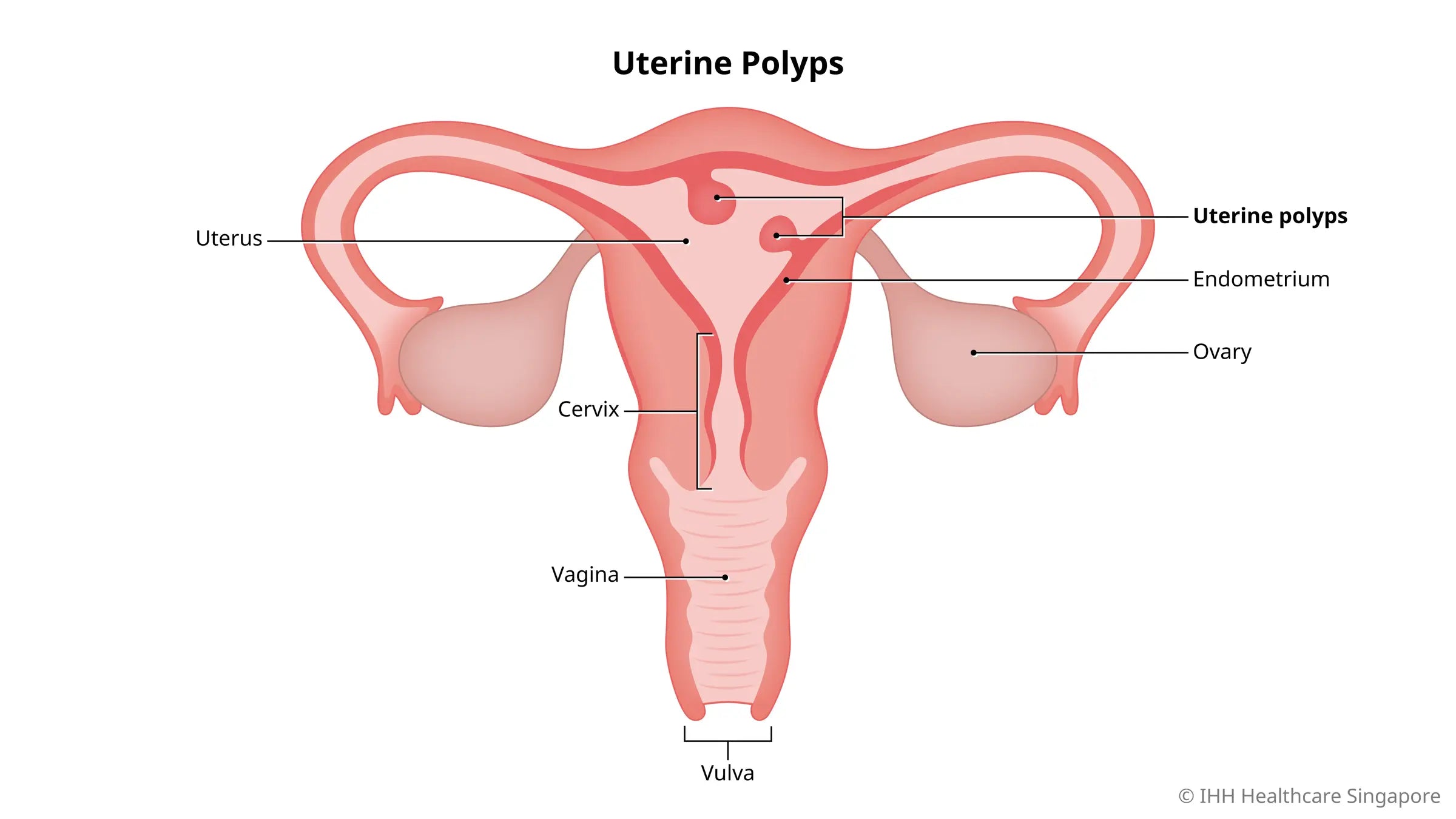
What is a uterine (endometrial) polyp?
Uterine polyps, also called endometrial polyps, are soft growths that arise from the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. Polyps may have a broad base that grows from the uterine lining or a thin body that extends into the uterine cavity.
In general, uterine polyps are benign or noncancerous, but they can cause problems with menstruation and fertility.
Menstruating women often have polyps, and polyps are less common in postmenopausal women.
Uterine polyps vs. uterine fibroids
Like uterine polyps, fibroids are tumors that do not arise from the lining of the uterus. Fibroids are muscle tumors in the wall of the uterus.
In addition to heavy bleeding, fibroids can also cause pain, difficulty urinating, and constipation.
What are the symptoms of uterine (endometrial) polyps?
If you have uterine polyps, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Irregular menstruation
- Heavy bleeding during menstruation
- Bleeding or spotting between periods
- Spotting or vaginal bleeding after menopause
- Infertility
What causes uterine (endometrial) polyps?
The exact cause of uterine polyps is unknown.
However, changes in estrogen levels have been linked to endometrial polyps. This is because estrogen is a hormone that stimulates the growth of the lining of the uterus. Excessive growth of the lining of the uterus is thought to be the cause of endometrial polyps.
What are the risk factors for uterine (endometrial) polyps?
Risk factors for uterine polyps include:
- Obesity
- Bag polycystic ovary syndrome
- High blood pressure
- Use of tamoxifen, a drug used to treat breast cancer
How are uterine (endometrial) polyps diagnosed?
Your doctor can diagnose uterine polyps using one of the following tests:
- Transvaginal ultrasound . This technique involves inserting a small, handheld device called an ultrasound probe into the vagina. The device produces sound waves and provides images of the inside of the uterus.
- Ultrasound of uterine cavity irrigation. This technique involves injecting fluid into the uterus through a catheter or thin tube. This relaxes the uterus and helps provide clear images of the uterus during a transvaginal ultrasound.
- Hysteroscopy . This technique involves inserting a hysteroscope through the vagina and cervix into the uterus, allowing the doctor to see inside the uterus.
- Endometrial biopsy. The suction catheter is used to take a sample of polyp tissue to test for cancer cells.
- Curettage . Using a curette (a long metal instrument with a small rim at one end), your doctor will take a tissue sample of the polyp and send it to a lab for analysis.
Size of endometrial polyp
While some studies suggest that uterine polyps larger than 1.5 cm in diameter may have a higher risk of malignancy, there is no conclusive evidence to prove that all polyps of this size are cancerous.
How are endometrial polyps treated?
Depending on your condition, your doctor may recommend the following measures:
- Stay alert. If you have small polyps that don't cause symptoms, you may not need treatment. Over time, small polyps may go away on their own. However, you may need to have them checked periodically.
- Take medication. Your doctor may recommend certain hormonal medications to regulate your hormone balance and reduce symptoms. However, symptoms may return after stopping the medication.
- Surgery. Your doctor may remove polyps surgically during a diagnostic procedure, such as a hysteroscopy or curettage. If you are postmenopausal and at high risk for uterine cancer, your doctor may decide to remove polyps.
If cancer cells are found in the polyp, your doctor may recommend a hysterectomy (surgical removal of the entire uterus) or other appropriate treatment options.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
👉 Contact SunCare for medical support and advice as well as professional private jet transportation services 🇸🇬 SUNCARE PTE. LTD SINGAPORE
🏠 Add: 10 Anson Road, #10-11 International Plaza, Singapore 079903
☎️ Hotline: +65 96727717 (Dr. Lien Minh - Director) Zalo, Viber
📨 Email: suncarehealth@gmail.com






