Stomach flu & food poisoning (Gastroenteritis)
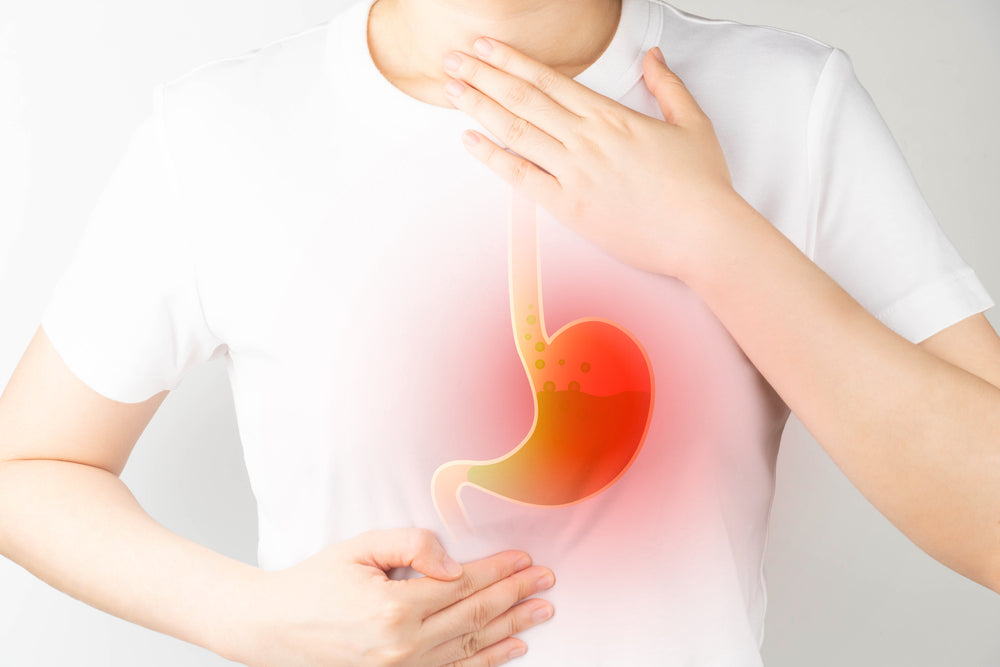
What is gastroenteritis?
Gastroenteritis is an infection that causes inflammation of the stomach or intestines. It can happen to anyone but is more common in children and older adults because of their weaker immune systems.
Depending on the cause, the illness may also be called stomach flu (gastroenteritis) or food poisoning.
What are the symptoms of stomach flu or food poisoning?
In general, the symptoms of stomach flu and food poisoning are similar and may include:
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomit
- Headache
- Watery diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and cramps
In rare cases, the stomach flu can cause severe dehydration. Watch for symptoms:
- Dizzy
- Dry mouth
- Sunken eyes
- Very thirsty
- Blurred vision
- Unable to think clearly or concentrate
- Reduced urine output
When to see a doctor?
You need to come to see a doctor Emergency Department If:
- You are pregnant.
- You have a fever above 38°C.
- You have vomiting that lasts more than a day.
- You have diarrhea that lasts more than 2 days.
- You have severe abdominal pain.
- You vomit blood or have blood in your stool.
- You have chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, kidney disease or heart disease
Stomach flu in children can lead to serious conditions. You should take your child to see a doctor if your child shows symptoms. any of the following symptoms :
- Vomiting green fluid
- Vomiting blood or having blood in the stool
- Fever above 38°C
- Diarrhea lasting longer than 2 weeks
- Feeling lethargic or drowsy a lot
- Severe or persistent abdominal pain
- Sunken fontanel (soft spot on top of skull)
- Persistent vomiting and inability to keep fluids down
- Diarrhea in large amounts more than 8-10 times a day
- Signs of dehydration such as little urine, dry lips and tongue, sunken eyes
What causes gastroenteritis?
In general, gastroenteritis can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites:
Stomach flu
Stomach flu is caused by Viruses , such as rotavirus or norovirus, cause it. Norovirus is the most common cause of acute gastroenteritis. Other viruses include astrovirus and adenovirus. Symptoms usually appear within 1 – 3 days after exposure to the virus.
Viral gastroenteritis can be transmitted through:
- Physical contact with an infected person
- Contact with contaminated objects, such as eating utensils and toys
Food poisoning
Food poisoning due to bacteria, viruses, or parasites caused by contaminated food. Symptoms usually appear within 1 hour – 7 days after eating
Common sources of food poisoning include:
- Unwashed fruits or vegetables
- Raw eggs, meat, fish or shellfish
- Cold rice not heated enough
- Soft cheese or unpasteurized milk
What are the complications and associated diseases of gastroenteritis?
Gastroenteritis can cause serious, even life-threatening, complications in vulnerable people, including:
- Children
- Pregnant women
- People who are taking immunosuppressive drugs
- People with weakened immune systems
- Elderly people
Children and infants are particularly at risk for severe symptoms from gastrointestinal infections because they become dehydrated much more quickly than adults.
How to prevent gastrointestinal inflammation?
Gastroenteritis cannot be completely prevented, although vaccines are available for some of the viruses that cause it. For example, it can be given to children 3 – 8 months Use rotavirus vaccine to prevent severe cases of rotavirus gastroenteritis.
Besides vaccination, you can prevent gastroenteritis by:
- Avoid raw or undercooked food
- Avoid physical contact with people with gastrointestinal infections
- Maintain good hygiene practices such as frequent hand washing
- Disinfect surfaces such as kitchen counters or desks regularly
- Wash your hands before cooking or handling food
- Separate live food and ready-to-eat food.
- Keep perishable foods cool or frozen immediately.
- Do not share cups or eating utensils
Note: It is possible to get gastroenteritis more than once because there are many strains of viruses that cause gastroenteritis.
How is gastroenteritis treated?
In most cases, gastroenteritis will clear up on its own. For symptom If the gastroenteritis is severe or persistent, antibiotics may be prescribed if the gastroenteritis is not caused by a virus.
For gastroenteritis in young children, avoid using over-the-counter medications to stop vomiting or diarrhea. See your doctor if symptoms do not improve or if the child can not hold water
Treat mild symptoms
How to treat mild symptoms of gastroenteritis:
- Increase your fluid intake, but drink small amounts frequently . Try to drink water every 30 minutes to 1 hour. Do not drink too much at once to avoid vomiting. An alternative to water is a frozen popsicle.
- Rehydrate with electrolytes . Oral rehydration solutions or sports drinks can help replenish fluids and electrolytes. However, try to avoid sugary drinks. If you are caring for a baby, ask your doctor which solution is best for your baby.
- Eat easily digestible foods . After the nausea has subsided, eat easily digestible foods such as rice, potatoes, toast, and bananas. Slowly return to your normal diet as you begin to feel better. Avoid alcohol, caffeine, and foods high in sugar or fat.
- Consider using probiotics
- Get plenty of rest .
When do you need medical attention?
If symptoms persist, or if in doubt, discuss with your doctor or visit a Emergency Department
If your child has diarrhea For more than 1 week , eliminate milk and all milk products for about 2 weeks. This is because some babies have a short-term intolerance to milk after a prolonged bout of gastrointestinal inflammation. Alternatives to milk include soy milk or lactose-free formula.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
👉 Contact SunCare for medical support and advice as well as professional private jet transportation services 🇸🇬 SUNCARE PTE. LTD SINGAPORE
🏠 Add: 10 Anson Road, #10-11 International Plaza, Singapore 079903
☎️ Hotline: +65 96727717 (Dr. Lien Minh - Director) Zalo, Viber
📨 Email: suncarehealth@gmail.com






