Gout
What is gout?
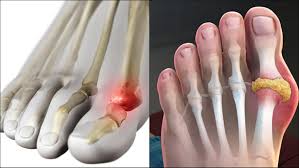
Gout is a form of crystal-induced arthritis that affects the joints. High levels of uric acid in the blood can lead to uric acid building up in the joints, causing inflammation and severe pain.
Gout is the most common form of arthritis. It commonly affects the following joints:
- Forefoot
- Foot
- Ankle
- Heel
- Instep
- Knee
Although less common, gout can also affect joints in the upper extremities such as the fingers or wrists.
Gout can cause sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in a joint. The affected joint may be so tender that it makes it difficult to turn over in bed or wakes you up in the middle of the night with a burning sensation in your big toe.
What are the symptoms of gout?
The first sign of a gout attack is a sudden, sharp, burning sensation in the affected joint.
This pain can quickly become severe, causing the joint to swell and become red. The initial pain usually goes away completely within a week.
Other symptoms include:
- Pain and difficulty walking during an acute gout attack.
- Uric acid crystals (tophi) of very large size appear in joints or other tissues.
- Chronic, ongoing pain with reduced mobility in the affected joint.
- Sensitive skin is sore, sensitive and painful the area around the joint, which can be extremely painful to the touch.
What causes gout?
Gout occurs when there is too much uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is produced by the body when it breaks down purines, common chemical compounds found in foods and drinks.
Normally, uric acid passes through the kidneys. However, a diet high in purines can cause excess uric acid in the blood, which cannot be excreted in the urine.
Excess uric acid builds up in the joints, forming crystals called tophi. These crystals cause inflammation, swelling, and pain.
What are the risk factors for gout?
Risk factors for gout include:
- Purine-rich diet lots of red meat, organ meats, seafood, beer, and fructose (fruit sugar).
- Obesity , a condition that causes the body to produce more uric acid, also makes it harder for the kidneys to excrete uric acid.
- Pathologies such as congestive heart failure, high blood pressure, diabetes, metabolic disease, and kidney disease.
- Certain medications Medications such as aspirin and thiazide diuretics (often prescribed for high blood pressure), can increase uric acid levels.
- Family history of gout also increases the risk of gout.
- Gender , in which men are more likely to develop gout between the ages of 30 and 50. Postmenopausal women also face a higher risk.
What are the complications and related diseases of gout?
If left untreated, gout can lead to complications such as:
- Joint damage , leading to deformity and limited mobility.
- Accumulation of uric acid crystal deposits subcutaneous.
- Accumulation of uric acid crystals in the urinary tract , leading to kidney stones.
- Gout attacks may recur , with frequency increasing if uric acid levels are not reduced.
- Impaired kidney function or kidney failure.
-
High blood pressure.
How to prevent gout?
Gout cannot be completely prevented. However, lifestyle changes can help reduce the severity and frequency of gout attacks.
You can reduce your risk of gout by:
- Limit or avoid alcoholic beverages , especially beer.
- Limit or avoid sugary drinks , especially those containing high-fructose corn syrup.
- Limit meat intake , especially red meat, organ meats and seafood.
- Maintain a healthy body weight . If you need to lose weight, avoid fasting or sudden weight loss, as this can temporarily increase uric acid levels.
- Increase your water intake and consume low-fat dairy products . These foods help prevent gout.
How is gout diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests for gout include:
- Synovial fluid test , which checks fluid extracted from the affected joint for urate crystals.
- Blood test to see if the levels of uric acid and creatinine in the blood are high. However, blood tests may not be conclusive, because some people with high uric acid levels do not have gout, while others may have gout even if their uric acid levels are not high.
- X-rays , although not typically used to diagnose gout, may be helpful in ruling out other potential causes of joint inflammation and pain.
- Ultrasound of musculoskeletal structures to detect urate crystal deposits in the joints.
- Dual-energy computed tomography (CT) to produce high-quality images that can detect urate crystals in joints even when the joint is not inflamed.
How is gout treated?
In spite of there is no cure gout, the symptoms of which can be control through dietary changes and medication.
Diet
Avoid foods and drinks high in purines to reduce your risk of gout. Foods high in purines include:
- Alcoholic beverages , especially beer and spirits.
- Red meat and organ meats , such as liver and kidneys, are high in saturated fat.
- Seafood , especially shellfish such as shrimp, lobster, mussels, anchovies, and sardines.
- Products with high fructose content such as soda and some fruit juices, cereals, ice cream, candy, and fast food.
Medicines
Your doctor may also recommend the following medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for acute gout attacks or in lower doses to help prevent future gout attacks. Because NSAIDs have been linked to stomach pain and ulcers, they should be used with caution.
- Analgesic such as colchicine at low doses to effectively relieve pain and prevent future gout attacks. When used in high doses, colchicine can cause serious side effects.
- Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and therefore pain. Corticosteroids can be taken as pills or injected into the affected joint. Side effects include mood changes, increased blood sugar levels, and increased blood pressure.
Depending on the severity of symptoms or frequency of attacks, other medications may be prescribed to help prevent the body from producing uric acid or improve the body's ability to remove uric acid.
Surgery
Surgery is rarely used to treat gout. However, surgery is sometimes needed to remove infected uric acid crystals or crystals that are blocking joint movement.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
👉 Contact SunCare for medical support and advice as well as professional private jet transportation services 🇸🇬 SUNCARE PTE. LTD SINGAPORE
🏠 Add: 10 Anson Road, #10-11 International Plaza, Singapore 079903
☎️ Hotline: +65 96727717 (Dr. Lien Minh - Director) Zalo, Viber
📨 Email: suncarehealth@gmail.com






